Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
In critical care, every second counts. Families often face the overwhelming challenge of ensuring their loved ones receive safe and timely treatment when traditional support systems fail. For patients with life-threatening heart or lung failure, standard ventilators and medication may not be enough to keep them stable. This is where extracorporeal membrane oxygenation comes in, a technology that has transformed the way critically ill patients are cared for.
Consider a patient who has just survived cardiac arrest or a child battling severe respiratory failure. The difference between survival and tragedy can often be the availability of ECMO transfers in an air ambulance. This technology not only keeps the heart and lungs functioning but also allows safe travel to specialized hospitals that can continue advanced treatment. In the world of emergency medicine, ECMO has become a lifeline.
What is ECMO? A Lifeline for Critical Transport
When families hear the word ECMO for the first time, it often comes during a medical emergency, which can feel overwhelming. So, what does ECMO mean? The term stands for Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. In simple terms, it is a special type of life support that helps the heart and lungs rest when they are too weak to function on their own.
The ECMO medical meaning is best understood by looking at what the machine does. It takes blood out of the body, adds oxygen, removes carbon dioxide, and then sends the clean blood back in. This process gives the body the oxygen it needs while letting the patient’s heart and lungs recover.
During long-distance transfers between hospitals, ECMO becomes a lifeline. Patients who are critically ill can remain stable on ECMO while being safely flown to a center that can provide advanced treatment. Without this support, many of these patients would not survive the journey.
How ECMO Work?
Understanding how ECMO works can reassure families that their loved one is safe during an air transfer. The process can be broken down into a few clear steps:
- Blood Withdrawal – A cannula (tube) is placed in a large blood vessel, and blood is gently drawn out of the patient’s body.
- Oxygenation – The blood passes through a special membrane oxygenator, which acts like an artificial lung, adding oxygen and removing carbon dioxide.
- Circulation – The oxygen-rich blood is then pumped back into the patient’s body, supporting vital organs.
- Continuous Monitoring – Onboard specialists monitor oxygen levels, blood flow, and patient stability at every moment of the journey.
When used inside an air ambulance, ECMO machines are securely installed and supported with backup systems. This ensures uninterrupted life support, even during turbulence or altitude changes. The ability of ECMO to maintain stable heart and lung function is what allows critically ill patients to safely undergo planned air transfers.
Conditions Treated by ECMO in Air Ambulances
ECMO is not designed for every medical emergency, it is reserved for situations where survival depends on extraordinary intervention.
In the setting of an air ambulance, its role becomes even more defined: supporting patients whose heart or lungs have reached a point where standard treatments no longer suffice. The conditions most often treated with ECMO during air transfers include:
- Severe Respiratory Failure such as Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
- Cardiac Arrest Recovery when the heart cannot pump effectively
- Post-Cardiac Surgery Complications where the heart or lungs need extra support
- Severe Pneumonia or Viral Infections that damage lung function
- Pulmonary Embolism or major blockages in lung blood vessels
- Newborn or Pediatric Critical Cases where advanced support is necessary
Patients are typically placed on ECMO in a hospital before being transferred. Every type of ambulance then provides a bridge, keeping the patient stable until they reach the specialist unit. This selective use ensures that only those who truly need ECMO receive it.
Types of ECMO
ECMO is not a single method but comes in two main types. Each type is used for different patient needs, and both can be supported during air ambulance transfers:
- Veno-Venous (VV) ECMO – This type supports only the lungs. Blood is taken out, oxygen is added, carbon dioxide is removed, and then the blood is returned through the veins. It is commonly used when the lungs are failing but the heart is still functioning.
- Veno-Arterial (VA) ECMO – This type supports both the heart and the lungs. Oxygen-rich blood is returned through the arteries, helping the heart circulate blood throughout the body. It is needed when both the heart and lungs are too weak.
The choice between VV and VA ECMO depends on the patient’s condition. Air ambulances equipped with ECMO can safely provide either option, ensuring the right kind of support during critical transfers.
Requirements for Using ECMO in an Air Ambulance
Transporting a patient on ECMO is not the same as a regular medical flight. It requires precise coordination and advanced systems. The key requirements include:
- Specialized Equipment – Portable ECMO machines, advanced ventilators, defibrillators, and monitoring devices.
- Power Supply and Backup Systems – Aircraft are equipped to support continuous machine operation without interruption.
- Secure Installations – ECMO machines are mounted safely to withstand flight conditions.
- Expert Handling – Only highly trained professionals can initiate and manage ECMO during transport.
These requirements ensure patient stability throughout the journey, even in complex cases like organ transfers.
Comprehensive Team & Equipment for Safe ECMO Transfers
Behind every successful ECMO transfer is a team working in perfect harmony. This team usually includes:
- Critical Care Nurses – Constantly monitor vitals, adjust medications, and comfort patients.
- Perfusionists – Specialists who manage the ECMO machine and ensure blood circulation remains safe and effective.
- Physicians – Intensivists and cardiologists oversee the patient’s overall condition and make critical decisions during flight.
Equally important is the coordination between the referring hospital and the receiving hospital. Before the transfer, medical teams share patient reports, ECMO settings, and anticipated challenges. On arrival, the receiving team is fully prepared to continue care without delay. This collaborative approach is what makes ECMO air transfers safe and effective.
Key Benefits of Air Ambulance ECMO Services
Families often ask why ECMO in an air ambulance is worth the effort. The benefits are significant:
- Uninterrupted Life Support – The patient remains on ECMO throughout the journey, preventing deterioration.
- Rapid Access to Specialized Care – Patients are quickly moved to centers equipped for advanced treatment.
- Expert Medical Oversight – Continuous monitoring ensures immediate response to any complication.
- Safe Long-Distance Transfers – Critical patients can travel across states or even countries without added risk.
- Seamless Integration with Other Services – ECMO transfers can be combined with commercial stretcher transfer or ground ambulances for complete door-to-door care
Potential Risks of ECMO During Air Transport
When a patient’s life is counting on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, even the smallest detail matters. Air transport introduces variables that a ground ICU never faces; such as altitude, confined spaces, and the need for flawless coordination. Understanding these risks is not about raising fear; it is about preparing for every scenario so that patient safety remains uncompromised.
Equipment Compatibility in Flight
ECMO machines are built for hospital settings, not aircraft cabins. Once in the air, factors like turbulence, restricted space, and power supply can affect performance. To keep the system safe and effective, equipment must be adapted for aviation use.
Important precautions include:
- Securing the ECMO circuit to avoid damage from vibration
- Guaranteeing a reliable power supply throughout the flight
- Using compact, flight-approved machines without losing efficiency
Patient Stability Across Altitudes
The human body responds differently in flight compared to the ground. Changes in cabin pressure, movement, and noise may seem minor for most people, but for patients on ECMO, these changes can have a significant impact.
Key concerns include:
- Shifts in blood pressure during ascent and descent
- Fluctuations in oxygen levels that require constant adjustments
- Extra strain on patients who are already in a delicate condition
Because of these factors, the care team must monitor and fine-tune ECMO settings continuously during the journey.
Communication Between Hospitals
An ECMO transfer is more than just moving a patient; it also means handing over an entire support system. If the sending and receiving hospitals do not communicate clearly, essential information can be lost.
Risks from poor coordination include:
- Delays in restarting treatment after arrival
- Incorrect ECMO settings due to missing details
- Greater stress for families expecting smooth continuity of care
What to Expect: The Patient and Family Journey During ECMO Transfer
When someone you love is being moved on ECMO, the unknown can feel frightening. A clear outline of what happens during the transfer can ease that worry.
Initial Assessment
The process begins with doctors reviewing the patient’s health and deciding if ECMO air transport is safe and necessary.
Pre-Transfer Coordination
Before the flight, both hospitals talk through the patient’s treatment history and ECMO settings so nothing is left uncertain.
Ground Ambulance Pickup
A ground ambulance then carefully moves the patient from the hospital to the air ambulance, with medical staff present every step of the way.
In-Flight Monitoring
During the flight, the team keeps a close eye on vital signs while ensuring ECMO support continues without interruption.
Landing and Handover
Once the plane lands, another ground ambulance immediately takes the patient to the receiving hospital for continued care.
Family Updates
Throughout the transfer, families are given regular updates so they feel connected and supported during the journey.
Why Choose RED Air Ambulance for ECMO Transfers?
RED Air Ambulance has gained trust by managing some of the most critical patient journeys. Its strength lies not only in advanced equipment but also in a clear focus on safety and compassion.
- Advanced Capabilities – Every aircraft carries essential systems like ECMO machines, ventilators, and other critical care tools.
- Skilled Professionals – Nurses, perfusionists, and doctors work together to handle complex medical situations with precision.
- Seamless Coordination – The entire journey, from hospital pickup to final handover, is planned in detail to avoid delays.
- Patient-Centered Care – Families receive regular updates and reassurance, keeping them involved throughout the transfer.
With years of experience and a strong record of safe operations, RED continues to be a trusted partner for families during the most difficult times.
Conclusion
patients with failing hearts or lungs, it represents a second chance at survival. When combined with air ambulance services, ECMO becomes more than just a machine—it is a bridge that allows patients to reach advanced hospitals safely and on time.
By understanding what is ECMO, how ECMO works, and the careful planning behind every transfer, families can feel confident in the process. In critical moments, ECMO means hope. And with RED Air Ambulance, that hope travels safely to where it is needed most.
FAQs
Q1. What is the purpose of ECMO?
Ans: The purpose of ECMO is to temporarily replace the function of the heart and lungs, giving them time to rest, heal, and recover safely.
Q2. How long can a person stay on ECMO?
Ans: A person can stay on ECMO from a few days to several weeks, depending on their condition, recovery progress, and medical team’s assessment.
Q3. Is ECMO considered life support?
Ans: Yes, ECMO is a form of life support that takes over heart and lung functions, keeping patients alive when these organs cannot work properly.
Q4. What is the survival rate for ECMO?
Ans: Survival rates for ECMO vary between 50 to 70 percent, depending on the patient’s age, underlying illness, and how quickly ECMO support begins.
Q5. Is ECMO high risk?
Ans: Yes, ECMO carries risks like bleeding, infection, or organ complications, but with expert teams and strict monitoring, it offers critical support in severe cases.


 18001207004
18001207004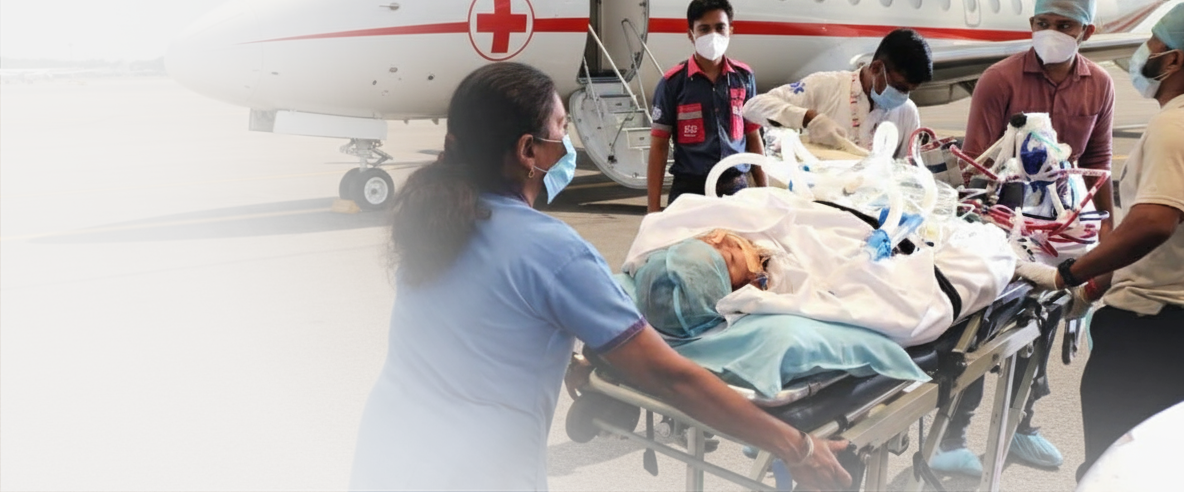
 September 9, 2025
September 9, 2025 Red Health
Red Health